Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone, playing a crucial role in developing traditionally male characteristics.
Although both males and females produce testosterone, levels are naturally higher in those assigned male at birth.
Testosterone is produced mainly by the gonads. Gonads are the sex organs of each sex.
For males, testosterone will be produced by the testicles. For women, it will be produced in the ovaries.
Yes, in specific cases. Women with low libido or menopausal symptoms may benefit from low-dose compounded creams.
Our pharmacy specializes in this type of medication.
Yes. For men, high testosterone levels can reduce sperm count. For women, high testosterone can alter the menstrual cycle and influence PCOS.
However, low testosterone can also negatively influence fertility.
Results are not immediate. Most patients start seeing differences in energy and mood withing 2-8 weeks.
While physical results such as increases in muscle mass and sexual function can take months.
Causes include aging, injury to testicles, chronic illnesses (diabetes, obesity), hormonal disorders, and certain medications. Lifestyle factors, such as stress or poor sleep, can also contribute.
Menopause may also lead to low testosterone in women.
Possible side effects include acne, sleep apnea, urinary symptoms, swelling and more.
Regular monitoring with your doctor minimizes risks.
Testosterone plays a vital role throughout all stages of life.




Yes, women also produce testosterone.
Testosterone enhances libido and fundamentally affects ovarian function and bone strength in people assigned female at birth.
Most of the testosterone produced by the ovaries is converted into the female sex hormone known as estradiol.
For those adults assigned female at birth, an average value is less than 40 ng/dL. In women, high testosterone levels can lead to polycystic ovarian syndrome.
Women who experience low levels of testosterone often use topical creams to replenish their levels.

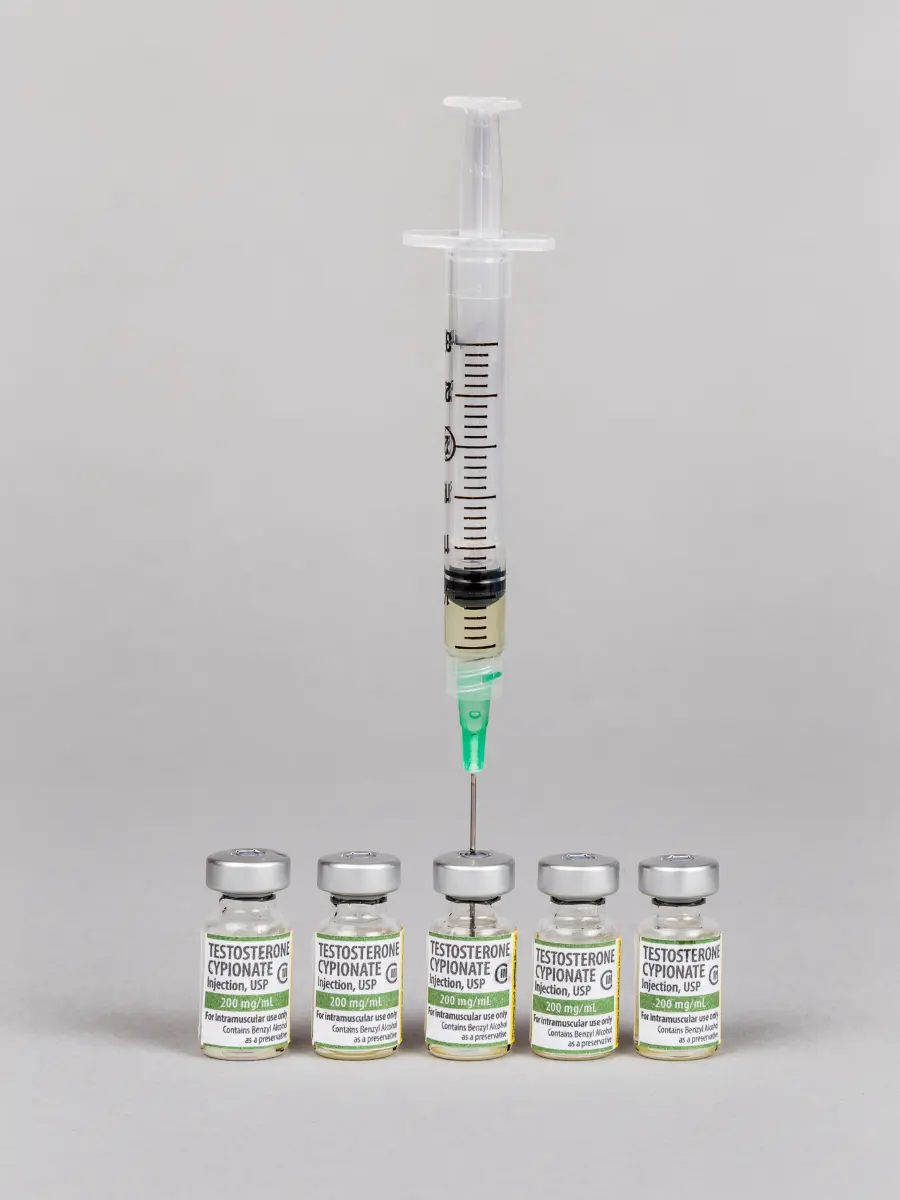

Low testosterone can be helped with testosterone replacement therapy (TRT). This type of hormone replacement therapy helps restore levels to a healthy standard.
Please feel free to reach out with any questions. You can complete the form below, and our staff will be happy to respond.
The holidays bring us joy, but they also bring us more prescriptions to fill and ship. Our pharmacy continues to work diligently, but an increase in demand may result in slightly longer processing times.
Please consider doing the following:
Thank you,
ClearSpring Team